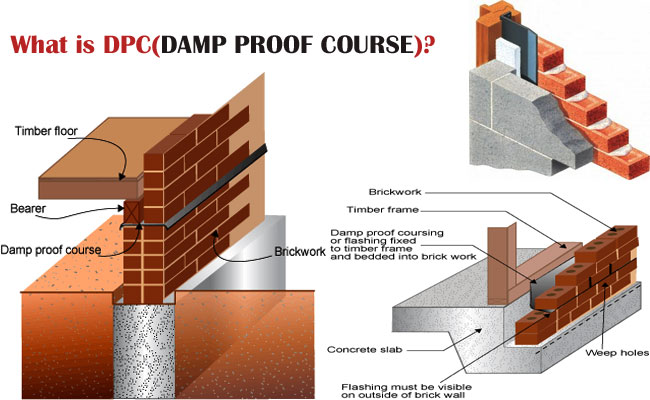
Definition, properties and advantages of DPC (Damp Proof Course)

DPC alias Damp Proof Course belongs to a horizontal barrier in a wall. The objective of DPC is to fight moisture that is swelling through the structure with capillary action.
Under this method, water repugnant membrane or damp proof course (DPC) is provided among the source of dampness and segment of building adjoining to it.
DPC may come in the form of bitumen, mastic asphalt, bituminous felts, plastic sheet, metal sheets, cement concrete.
DPC is arranged horizontally or vertically in floors, walls etc.
The following points should be kept in mind at the time of arranging DPC:-
- DPC should wrap full thickness of wall.
- Motar bed that provides support to DPC should have been levelled & uniform and does not include projections in order that DPC is not damaged.
- At junctions and corners of walls, the horizontal DPC (on floor) should be placed consistently.
- If a horizontal DPC is extended to vertical face, a cement concrete fillet of 7.5 cm radius should be arranged at junction.
- DPC should not be retained uncovered on wall surface else it will be damaged throughout finishing.
The following types of materials are applied for damp proof course:-
- Asphalts
- Bituminous felts
- Mortar
- Plastic, metal sheet etc.
In most of the buildings, DPC performs as a rich mix concrete, generally in the ratio of 1:1½:3 over the full width of the wall and the thickness fluctuates from 10 m to 15 cm (4 inches to 6 iches) with water resistant compound.
Superior quality DPC should contain the following features:-
- Should be properly impenetrable
- Should not allow entrance of moisture
- Material should be stable enough to withstand superimposed load or pressure
- Material should be compliant to adapt the structural movements devoid of any cracks
- Materials should be inexpensive
- Material should stand steady in its position