Types of Crush Stones (Ballast) and their functions in Railway Track

Definition of ballast
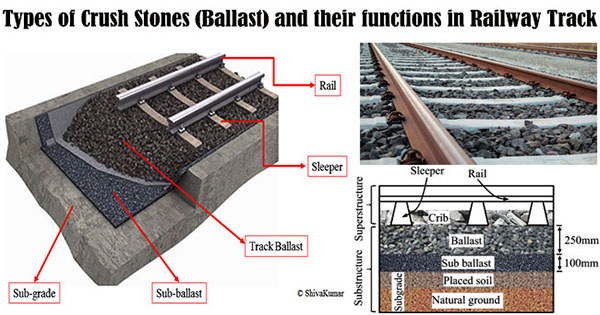
Railway Ballast stands for a layer combined with broken stone, moorum or any other gritty (sand) material which are set & packed underneath and around the sleepers for transmitting the loads from the wheels of trains and sleepers to the formation as well as arranging drainage & providing longitudinal & lateral strength.
Given below, the detail information about common types of ballast found in railways:-
Sand ballast
Sand ballast is mainly suitable for cast iron (CI) pots. It is also utilized with wooden and steel through sleepers in the regions where the density of traffic density is significantly weak. Coarse sand is recommended with regard to fine sand. It contains good drainage properties, but there is shortcoming of blowing off as the thickness of sand is very light. It also leads to extreme erode of the rail top and the movable segments of the rolling stock.
Moorum ballast
Due to the degradation of laterite, moorum is developed. Its color fluctuates from red to yellow. The moorum ballast is generally utilized as the preliminary ballast in new constructions as well as sub-ballast. Since it resists water from infiltrating into the development, it is also applied as a blanketing material for black cotton soil.
Coal ash or cinder
This type of ballast is mostly found in yards and sidings or as the primary ballast in new constructions as it is very inexpensive and readily accessible. It is not recommended for steel sleepers and fittings due to its erosive effect.
Broken stone ballast
This type of ballast is suitable for Indian Railways. Superior stone ballast is normally derived from rigid stones like granite, quartzite, and hard trap. The quality of stone should not be such that is it permeable nor does it flake off because of the changes in weather. Good quality hard stone is the prime materials for high-speed tracks. This type of ballast becomes inexpensive over time.
Other types of ballast
There exist other types of ballast ranging from the brickbat ballast, gravel ballast, kankar stone ballast, and even earth ballast. These types of ballast are mainly utilized in special occasions.
Benefits of Ballast
- To offer rigid and level bed for the sleepers to build on.
- To facilitate retaining exact track level devoid of affecting the rail road bed
- To discharge the water instantly and to maintain the sleepers in dry conditions
- To prevent the development of vegetation
- To retain the sleepers in exact location throughout the passage of trains
- To transfer and disperse the loads from the sleepers to the formation
- To allow lateral strength to the track overall