Basic difference among main bars and distribution bars

Because of the loading conditions the slab is susceptible to potential or sagging bonding movement on the bottom surface at the centre of the span and negative or hogging bending moment at top near supports. To counter these moments main reinforcement is arranged at bottom surface around the direction of span to defy positive bending moment.
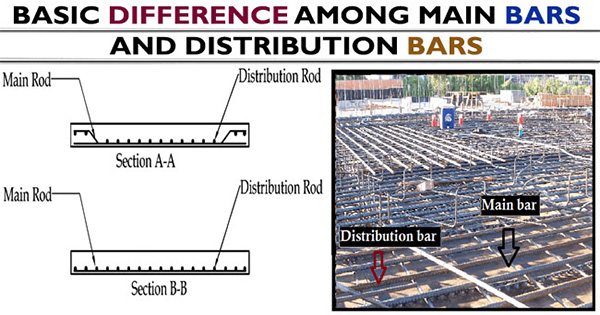
Given below, the major differences between the main bars and distribution bars:-
The main bars are arranged at lesser extent direction in the slab to transmit the bending moment produced at the bottom of the slab to beam.
For main bars, steel with high dimension is applied in the slab.
In one way slab, the support is given at one direction or one side and therefore, the main bar should be arranged at the lesser extent.
The main bars should withstand and carry all the tensile stresses, bending moment (sagging) as well as super imposed load (dead load) which are developed at the shorter span of the slabs.
The distribution bars are provided in the slab with the purpose of withstanding the shear stress as the cracks are formed to distribute stresses on the top of the bar and it should be arranged at the longer extent of the slab.
While designing slab, the thickness of main bar should not be under 8 mm for high yield strength deformed steel bars. If plain bars are used, the thickness should be 10 mm.
Distribution bars are placed at the top of the slab.
For distribution bars, lesser dimensions of the steel should be selected.
The purpose of distribution bars is to disperse the super imposed load constantly or withstand shrinkage stresses caused by variation in temperature in winter or summer.
The distribution bar is arranged to support the mesh as well as retain exact center to center gapping of main bars.